DNA Center – Deep Dive Learning.
What is DNA ( Digital Network Architecture) Centre ?
Its nothing but another cisco marketing tool converts your CLI commands to execute in GUI automated manner so there are no Human errors will occur during deployment or while doing changes (* but never mentioned anywhere – what if the machine makes mistake part of the process – like crashes while deploying, lost connection to end device while deploying …Big Factor for me Cost Model – I have not seen any Life Cycle or Replacement model which can explain what will happen exiting tools purchased already in Enterprise Like Prime so on.)
This tool enables the network admin to have a simplified integrated user experience across the entire enterprise portfolio of products.
Cisco DNA Center enables the network administrator to:
- Design your network using intuitive workflows
- Define user and device profiles that facilitate secure access and network segmentation based on business needs
- Policy-based automation to deliver services to the network based on business priority and to simply device deployment
- Assure network performance with real-time and historical data analytics, to provide actionable insights and detect problems before they happen along with Guided remediation actions for 100+ Insights
- Design and Deploy Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) to simplifies delivery of consistent, highly secure, identity-based policy for users and devices across wired and wireless networks
Intent Based Network (IBN)

DNA Center has 4 Major Componets



DNA Centre high level Menu

- DNA Design
| Network Hierarchy | Consists of Area, Building, Floor |
| Network Settings | Consists of Network, Device Credentials, IP address Pools, QoS , Wireless |
| Image Repository | IOS image repositor for Upgrade or Degrade ( always use Golden Image) |
| Network Profile | Standardized Configurations for Routers, Switches and WLCs |
| Authentication Template | Authentication pre-defined template to assigned for the device |
Sites – is the major part of DNA – it is very important to be Unique Profile (this required to be in the part of Design) –
- Building
- Area
Area – Must required to start DNAC
- Area 1
- Area 2
- Building
- Floor 1
- Floor 9
- Building 1
- Floor 5
- Building


Add Area

Add Building Example :

Adding Floor – and also you can add MAP directly drag and drop. – cool feature.

2. Design –> Network Settings

3. IP address Pools – DNAC has inbuilt IPAM Tool, it can also integrate with other vendor Like Infoblox.

POLICY
| Group-Based Access Control | Group-based access control policies are Security Group Access Control Lists (SGACLs). Cisco DNA Center integrates with Cisco ISE to simplify the process of creating and maintaining SGACLs. |
| IP Based Access Control | IP-based access control policies can be used to filter traffic for various purposes, including security, monitoring, route selection, and network address translation. |
| Application | Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the ability of a network to provide preferential or deferential service to selected network traffic |
| Traffic Copy | Using Cisco DNA Center, you can set up an Encapsulated Remote Switched Port Analyzer (ERSPAN) configuration such that the IP traffic flow between two entities is copied to a specified destination for monitoring or troubleshooting. |
| Virtual Network | virtual networks are isolated in routing and switching environments. You can use virtual networks to segment your physical network into multiple logical networks. Cisco DNA Center has a single virtual network, and all users and endpoints belong to this virtual network. If Cisco DNA Center is integrated with the Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), the default virtual network is populated with user groups and endpoints from Cisco ISE. |

POLICY –> Group-Based Access Control
- Scalable Group – Scalable groups comprise a grouping of users, end-point devices, or resources that share the same access control requirements. These groups (known in Cisco ISE as security group) are defined in Cisco ISE. A scalable group may have as few as one item (one user, one end-point device, or one resource) in it.
- Access Contracts – An access contract is a common building block that is used in both group-based and IP-based access control policies. It defines the rules that make up the access control policies. These rules specify the actions (permit or deny) performed when traffic matches a specific port or protocol and the implicit actions (permit or deny) performed when no other rules match.
- Policies – You can have policies based on the requirement – DNA also has a matrix as below

POLICY –>IP-Based Access Control Policies
- IP Network Groups – IP network groups comprise IP subnets that share the same access control requirements. These groups can be defined only in Cisco DNA Center. An IP network group may have as few as one IP subnet in it.
- Access Contract -An access contract is a common building block that is used in both IP-based and group-based access control policies. It defines the rules that make up the access control policies. These rules specify the actions (permit or deny) performed when traffic matches a specific port or protocol and the implicit actions (permit or deny) performed when no other rules match.
POLICY –> Application
- Application Policies – Quality of Service (QoS) refers to the ability of a network to provide preferential or deferential service to selected network traffic

- Queuing Profiles – Queuing profiles allow you to define an interface’s bandwidth allocation based on the interface speed and the traffic class.
POLICY –> Traffic Copy
- Traffic Copy Policy – To be monitored, a source scalable group that is used in a traffic copy policy needs to be statically mapped to the switches and their interfaces.
- Traffic Copy Destination – Layer 2 or Layer 3 LAN interface on a device that receives, processes, and analyzes the ERSPAN data. The device is typically a packet capture or network analysis tool that receives a copy of the traffic flow for analysis.
- Traffic Copy Contract – Depends on Contract copy of the destination.
POLICY –> Virtual Network
Only the assigned user groups are allowed to enter a virtual network. Within a virtual network, users and devices can communicate with each other unless explicitly blocked by an access policy. Users across different virtual networks cannot communicate with each other. However, an exception policy can be created to allow some users to communicate across different virtual networks.
A typical use case is building management, where the user community needs to be segmented from building systems, such as lighting; heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems; and security systems. In this case, you segment the user community and the building systems into two or more virtual networks to block unauthorized access of the building systems.

PROVISION – Provisioning devices includes the following aspects:
- Onboarding devices with Plug and Play, which adds them to the inventory.
- Deploying the required settings and policies to devices in the inventory.
- Adding devices to sites.
- Creating fabric domains and adding devices to the fabric.
| Devices | Devices discovered |
| Fabric | A fabric site is an independent fabric area with a unique set of network devices: control plane, border node, edge node, wireless controller, ISE PSN. Different levels of redundancy and scale can be designed per site by including local resources: DHCP, AAA, DNS, Internet. |
| Services | Services – like Stealthwatch / visibility/app hosting |
Devices

Fabric – Fabric or Transit/Peer Network below to manage, or add a new item by clicking ‘Add Fabric or Transit/Peer Network.
Services –

ASSURANCE – Assurance provides a comprehensive solution to assure better and consistent service levels to meet growing business demands. It addresses not just the reactive network monitoring and troubleshooting, but also the proactive and predictive aspects of running a network and ensuring optimal client, application, and service performance.
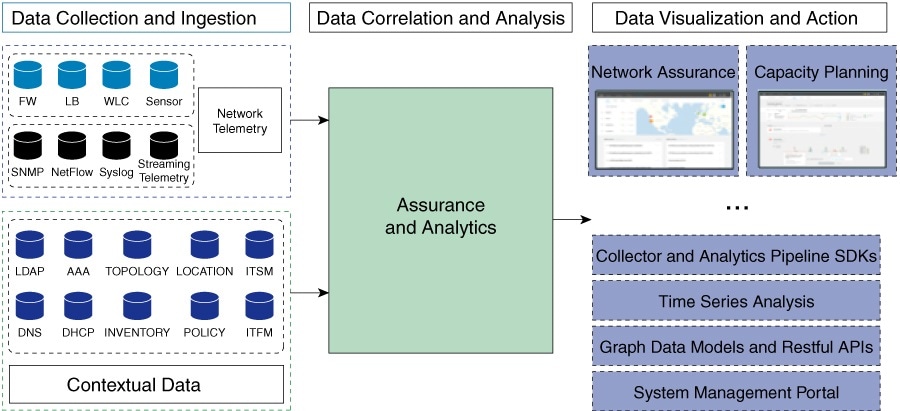


PLATFORM -Data Platform provides tools that can help you monitor and troubleshoot Cisco DNA Center applications. Data Platform displays synthesized data from various inputs to help you identify patterns, trends, and problem areas in your network. For example, if something goes wrong in your network, you can quickly get answers to questions such as whether a pipeline is in an error state and what is the real-time traffic flow in a particular area.

Training Passed :

More information to come – Happy Labbing…………….!